Abstract
Background:
The use of objective endpoints is critical for the generalization and clinical implications of a study. Overall survival (OS) has traditionally been used as the gold standard for demonstrating the true clinical benefit of a therapy or intervention. Use of clinically meaningful pre-specified endpoints is essential for a successful clinical trial. In this systemic review, we aimed to investigate different primary and secondary endpoints used in phase III randomized controlled trials (RCTs) for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT), and their trends over a span of 15 years.
Methods:
Following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines, a comprehensive literature search was conducted on three databases (PubMed, Cochrane, and Clinical trials.gov) using MeSH terms and keywords for "hematopoietic stem cell transplantation" AND "Randomized Controlled Trials as Topic" from January 2006 to May 2021. We screened 2223 articles. After excluding duplicates, reviews, and irrelevant articles, 170 articles reporting only phase III RCTs with primary and secondary endpoints on HCT were included for our systematic review. Primary and secondary endpoints data were extracted from the included studies and the frequency of various endpoints as well as their yearly frequencies were calculated. Disease-free survival (DFS) was used to represent similar outcomes including event-free survival (EFS), progression-free survival (PFS), leukemia-free survival (LFS), and relapse-free survival (RFS).
Results:
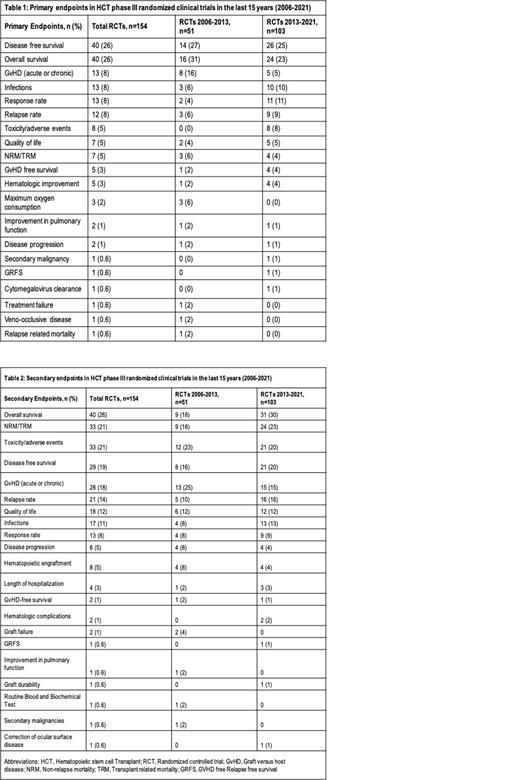
Our study included 154 phase III RCTs on HCT. DFS was the primary endpoint in 40 (26%) studies, while OS and graft versus host disease (GvHD) were reported as primary endpoints in 40 (26%) and 13 (8%) studies, respectively. Infections, response rate, relapse rate (RR), toxicity/adverse events, quality of life (QoL), non-relapse mortality (NRM)/transplant-related mortality (TRM), GvHD-free survival, and hematological improvement (HI) were used as primary endpoints in 13 (8%), 13 (8%), 12 (8%), 8 (5%), 7 (4.5%), 7 (4.5%), 6 (4%), and 5 (3%) studies respectively. Other infrequently reported
primary endpoints are listed in Table 1. Secondary endpoints followed a similar pattern as detailed in Table 2. OS (n=26, 40%), toxicity/adverse events (n=33, 21%), and TRM/NRM (n=33, 21%) were commonly reported secondary endpoints. DFS, GvHD, RR, QoL, infections, response rate, disease progression, and hematopoietic engraftment were used as secondary endpoints in 29 (19%), 28 (18%), 21 (14%), 17 (11%), 17 (11%), 13 (8%), 8 (5%), and 8 (5%) studies, respectively. After 2013, decrease in the use of DFS (27% to 25%) and OS (31% to 23%) as a primary endpoint was noted. For secondary endpoints, a higher trend in the use of OS (18% to 30%) and NRM/TRM (18% to 23%) was observed after 2013. (Table 2)
Conclusion:
Disease-free survival was the most common primary endpoint and overall survival was the most common secondary endpoint in phase III randomized controlled trials for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation over the last 15 years. The use of QoL as an endpoint remained low in RCTs. Newly introduced composite endpoint of GvHD-free relapse-free survival (GRFS) may be considered as a primary endpoint in future prospective studies.
Abhyankar: Incyte/Therakos: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. McGuirk: Pluristem Therapeutics: Research Funding; Bellicum Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Gamida Cell: Research Funding; Allovir: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Magenta Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Fresenius Biotech: Research Funding; EcoR1 Capital: Consultancy; Novartis: Research Funding; Kite/ Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel accommodations, expense, Kite a Gilead company, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Juno Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Astelllas Pharma: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal